ESPRI services ensure a solid and constant support to the French climate research, by preserving an attentive listening to the different research teams of IPSL and its partners. This approach also allows to create scientific synergies in order to collect the new needs of the community and propose original and structuring computing services.
ESPRI Community chart
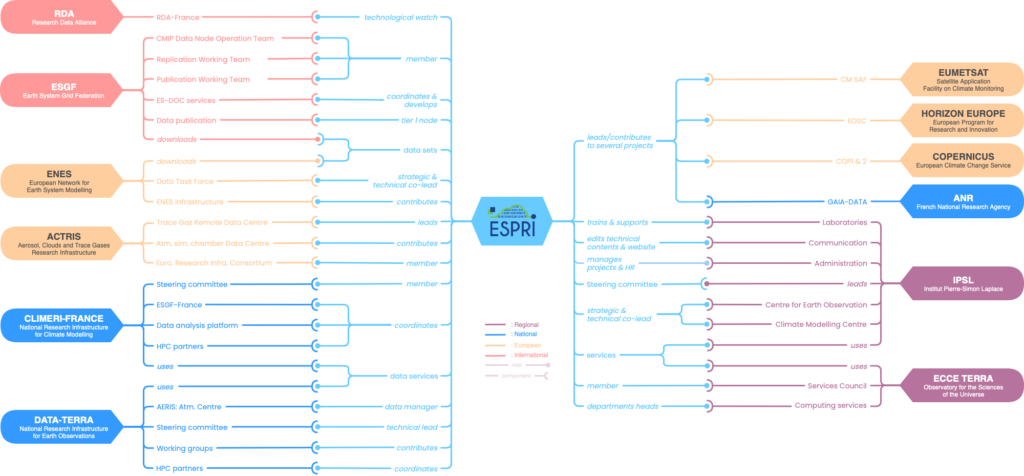
Regional landscape
The IPSL federation has different missions among them to develop and propose a set of regional, national and international computing and data services for research related to environmental and climate science. To fulfill these missions, ESPRI has been mandated by IPSL to administrate IT systems, network and manage data from the IPSL Climate Modeling Center (CMC) and Center for Earth Observation (CEO).
Center for Earth Observation
The Centre for Earth Observation supports and coordinates IPSL resources dedicated to measurement systems and observational data. In Earth observations, CEO plays a coordination role at the regional level to strengthen the collective Earth observation activities to improve our understanding of the climate system. CEO facilitates also the IPSL coordination for satellite missions to support ongoing missions and new space concepts, supports coordinated actions for long-term monitoring, supports the maintenance of long-term datasets and data management from multiple instruments, relying on ESPRI to manage and distribute the observational datasets.
Climate Modelling Centre
The Climate Modelling Centre explores physical, chemical and biogeochemical aspects of the Earth’s climate. It brings together modelling teams from the various IPSL laboratories who study the different parts of the climate system (atmosphere, ocean, continental surfaces, cryosphere) and their couplings. Studies focus on the functioning of the climate system, its variability and climate change, whether of natural origin or due to human activities by developing and using an integrated model of the Earth system to carry out climate simulations. These results are managed, analysed and distributed through ESPRI facilities for and within the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP) and the Coordinated Regional Climate Downscaling Experiment (CORDEX).
The IPSL activities of collecting, archiving and making available different types of data started in the 1990s. Since then, it has developed continuously beside the creation and growth of observatories in French universities (OSUs). The IPSL services have therefore gradually been integrated into the Ile-de-France OSUs. In particular the OSU Ecce Terra of INSU and Sorbonne University co-host some of the ESPRI facilities and services. In this context, ESPRI is a labelled platform of Sorbonne University and CNRS. The OSUs remain specific and respond to a regional integration and mutualisation of scientific platforms. It is therefore important in the Paris region to ensure coherence between the digital strategy plans of the IPSL and the OSUs.
ESPRI manages all the IPSL common IT resources on Sorbonne University and the Ecole Polytechnique sites. It has one dedicated room on each site to host the machines and ensure a fair administration of the resources, the network in agreement with the security constraints. Thus, ESPRI is at the interface between the IT Departments of the hosting sites and the IPSL laboratories.
National role
ESPRI is driven by the needs of the national and international scientific communities. The IPSL Computing and Data Centre is integrated into national, European and international Research Infrastructures (RI) to which ESPRI contributes and in which it represents the IPSL. In particular, it constitutes an essential building block for the following RIs and is one of the four Data and Services Centers for the AERIS national atmospheric data centre.
CLIMERI-France is structured around five main activities to ensure the production, analysis and dissemination of climate simulations, in close interaction with the international activity of the World Climate Research Program and the various users of these simulations. CLIMERI-France also relies on the modelling resources and expertise of:
- Centre National de Recherche Météorologique (CNRM),
- Centre Européen de Recherche et de Formation Avancée pour le Calcul Scientifique (CERFACS),
- Météo France,
- University of Louvain-la-Neuve (Belgium),
- Institut des Géosciences de l’Environnement (IGE),
- University of Bordeaux (EPOC),
- Laboratoire d’Océanographie Physique et Spatiale (LOPS),
- Laboratoire d’Etude en Géophysique et Océanographie Spatiale (LEGOS).
Data-Terra organises data access in an integrated way, by making available data products and services related to the observation of the Earth system, via four French data clusters: AERIS (Atmosphere), FORMATERRE (Solid Earth), THEIA (Continental Surfaces), ODATIS (Oceans and Coasts). Data-Terra also relies on resources and expertise of:
- Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES),
- Institut Français de Recherche pour l’Exploitation de la Mer (IFREMER),
- Institut National de l’information Géographique et Forestière (IGN),
- Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD),
- Institut National de Recherche Agronomique (INRAE
- Météo-France).
European influence
The European Networks for Earth System Modelling (ENES) gathers 47 partners from academic, public and industrial world to work together and cooperate to discuss strategies to accelerate progress in climate and Earth system modelling and understanding. ENES also relies on computing resources of:
- Centre for Environmental Data Analysis (CEDA – UK),
- Deutsche Klimarechenzentrum (DKRZ – Germany),
- Centro Euro-Mediterraneo sui Cambiamenti Climatici (CMCC – Italy),
- Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute (SMHI – Sweden),
- University of Cantabria (UCAN – Spain).
ESPRI is also involved in the ACTRIS-DC as a part of the European consortium to handle the ACTRIS data, operating the trace gases remote sensing data center unit (ACTRIS-GRES). ACTRIS is a pan-European research infrastructure producing high-quality data and information on short-lived atmospheric constituents and on the processes leading to the variability of these constituents in natural and controlled atmospheres. The primary role of ACTRIS DC is to compile, archive and provide access to well documented and traceable ACTRIS measurement data and data products, including digital tools for visualizations, data analysis and research. As a tool for science, the highest priorities for ACTRIS DC is to maintain and increase the availability of ACTRIS data and data products relevant to climate and air quality research for all interested users.
International engagement
The Earth System Grid Federation (ESGF) is an interagency and international collaboration that develops, deploys and maintains software infrastructure for the management, dissemination, and analysis of model output and observational data. ESGF also relies on the contribution and funding from:

